AWS Cloud Operations Certification Journey: Mastering Systems Manager
AWS Cloud Operations Certification Journey: Mastering Systems Manager
Introduction
As I continue my journey toward AWS Cloud Operations certification, I recently completed an intensive hands-on lab focusing on AWS Systems Manager - a comprehensive toolset for configuring and managing Amazon EC2 instances, on-premises servers, and other AWS resources at scale. Systems Manager provides a unified interface that allows you to easily centralize operational data and automate tasks across your AWS resources, making it an essential component of any cloud operations strategy.
In this post, I'll walk through the key capabilities I explored during the lab: Systems Manager Inventory, Run Command, Parameter Store, and Session Manager, providing practical insights into how these tools enhance operational efficiency and security.
Understanding AWS Systems Manager
AWS Systems Manager is a collection of capabilities designed to help you manage your AWS resources at scale. Whether you're managing EC2 instances, on-premises servers, or virtual machines in a hybrid environment, Systems Manager provides a centralized interface for configuration, management, and automation tasks. The service integrates seamlessly with other AWS services and provides comprehensive operational visibility without requiring direct system access.
Task 1: Using Systems Manager Inventory for Configuration Verification
What is Systems Manager Inventory?
AWS Systems Manager Inventory collects metadata from your Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers in your hybrid environment. This includes operating system details, applications installed, patches, custom attributes, and other instance metadata. You can query this information to understand which instances meet your software policies and which need updates.
Lab Experience
In my lab, I used Systems Manager Inventory to gather configuration details from a managed EC2 instance:
- Navigated to Systems Manager → Fleet Manager
- Selected the "Managed Instance"
- Configured an inventory association named "Inventory-Association" for that specific instance
- Reviewed the collected inventory data including installed applications

This process demonstrated how Inventory enables you to validate software configurations across your infrastructure without logging into each instance. Instead of manually connecting to dozens or hundreds of servers to check what's installed, you can query this information centrally through the AWS console or APIs.
Practical Benefits
- Compliance Verification: Quickly verify that all instances meet security and compliance requirements
- Software Asset Management: Track software licenses and ensure proper installation across environments
- Configuration Management: Identify configuration drifts across your fleet
- Security Assessments: Identify vulnerable software versions that need updating
Task 2: Automating Application Deployment with Run Command
Run Command Capabilities
AWS Systems Manager Run Command gives you the ability to remotely and securely manage the configuration of your managed instances at scale. You can run commands across a fleet of instances from a central location, which is particularly useful for patching, configuration changes, and other administrative tasks.
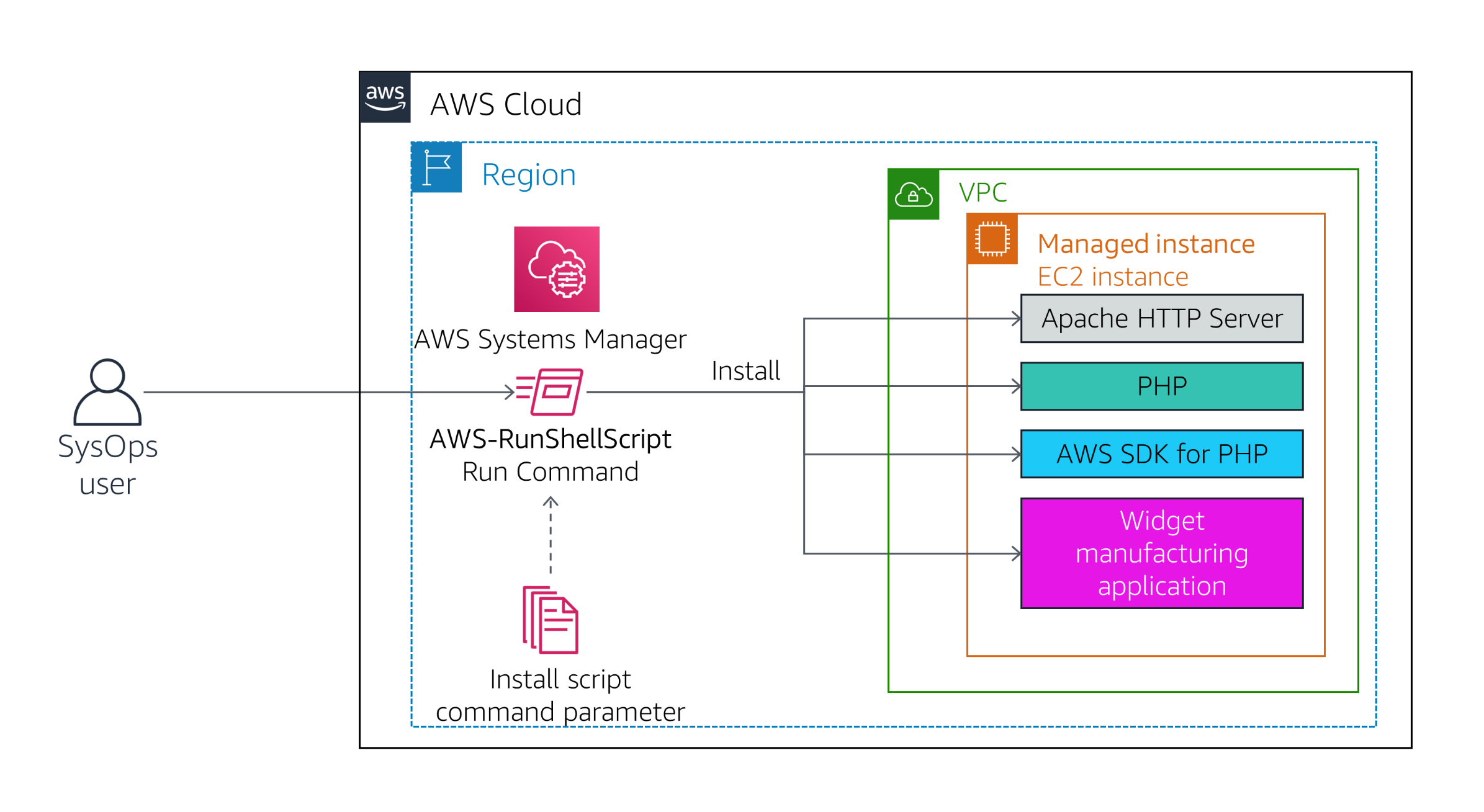
Lab Deployment Process
The most impressive part of the lab was deploying a custom web application (Widget Manufacturing Dashboard) using Run Command without logging into the instance. Here's what happened:
- Selected a pre-configured document named
InstallDashboardApp - Targeted the "Managed Instance"
- Executed the command that performed these actions:
- Installed Apache web server and PHP
- Activated the web server
- Installed the AWS SDK for PHP
- Installed the application files
Systems Manager Document Structure
The installation process was handled by a Systems Manager document using the following JSON schema:
{
"schemaVersion": "2.2",
"description": "Install Dashboard App",
"mainSteps": [
{
"inputs": {
"runCommand": [
" #!/bin/sh",
" # Install Apache Web Server and PHP",
" yum install -y httpd",
" amazon-linux-extras install -y php7.2",
" # Turn on web server",
" systemctl enable httpd.service",
" systemctl start httpd.service",
" # Download and install the AWS SDK for PHP",
" wget https://github.com/aws/aws-sdk-php/releases/download/3.62.3/aws.zip",
" unzip aws -d /var/www/html",
" # Download Application files",
" wget https://aws-tc-largeobjects.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/ILT-TF-200-ACSOPS-1/lab-1-ssm/widget-app.zip",
" unzip widget-app.zip -d /var/www/html/"
]
},
"name": "InstallDashboardApp",
"action": "aws:runShellScript"
}
]
}
Key Advantages
- No SSH Required: The installation happened without opening port 22 or managing SSH keys
- Centralized Execution: Commands run consistently across multiple instances
- Audit Trail: All command executions are logged for compliance and troubleshooting
- Scalability: The same command can be applied to hundreds of instances simultaneously
Task 3: Managing Application Settings with Parameter Store
Parameter Store Overview
AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store provides secure, hierarchical storage for configuration data and secrets management. You can store values such as passwords, database connection strings, and application settings as parameter values, with options to store them as plain text or encrypted data.
Dynamic Configuration in Action
In the lab, I created a parameter that dynamically enabled features in the deployed application:
- Created a parameter
/dashboard/show-beta-featureswith valueTrue - The application automatically detected this parameter and enabled additional features
- Refreshing the application showed an additional chart that was previously hidden
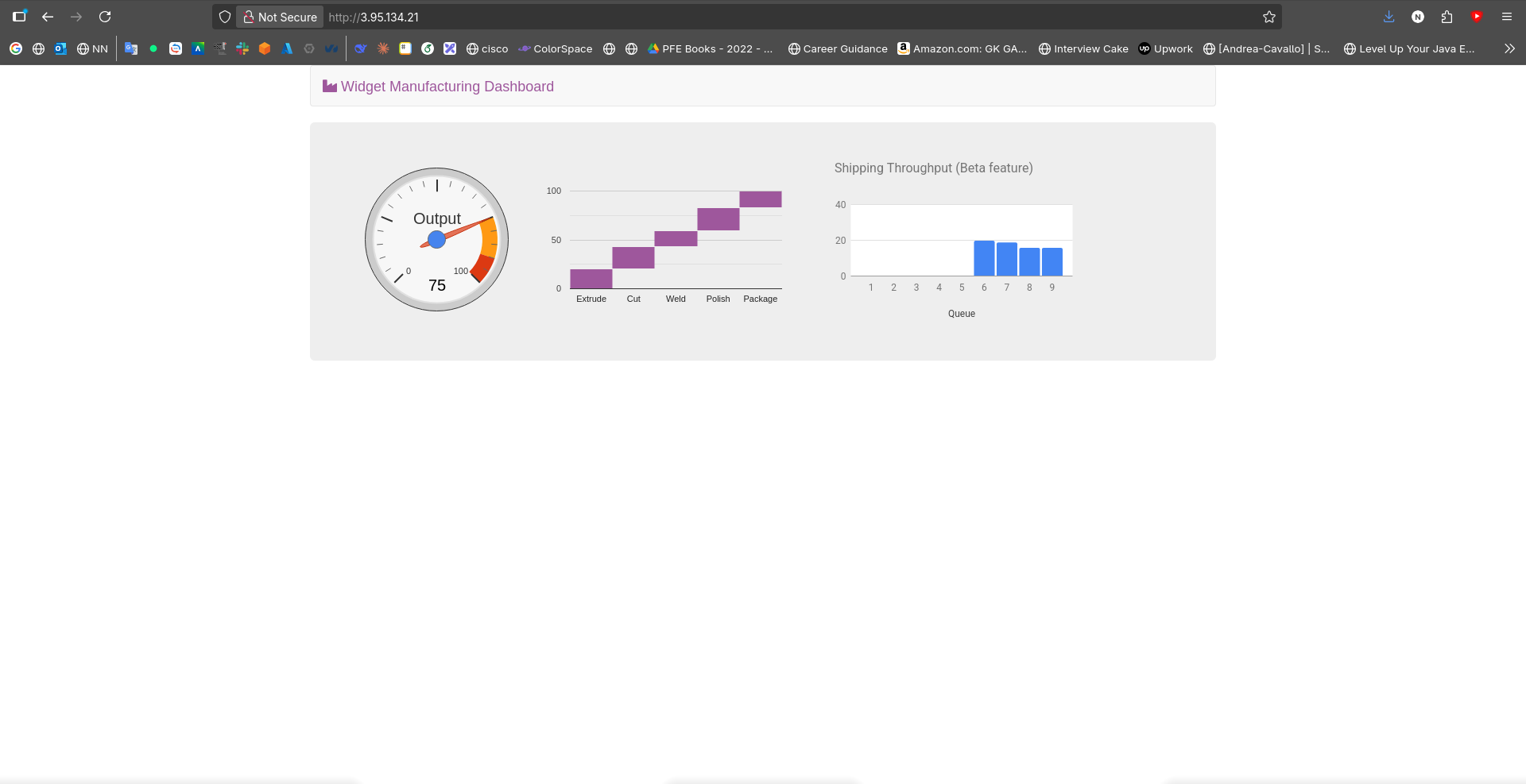
This demonstrates how Parameter Store enables dynamic configuration changes without redeploying applications. The application can check Parameter Store at runtime to determine which features to enable, allowing for dark launches and feature toggles.
Security Benefits
- Encrypted Storage: Sensitive parameters can be encrypted using AWS KMS
- IAM Integration: Fine-grained access control for who can read or modify parameters
- Version Control: Parameter Store maintains a version history of all changes
- Cross-Region Replication: Parameters can be replicated across regions for disaster recovery
Task 4: Secure Instance Access with Session Manager
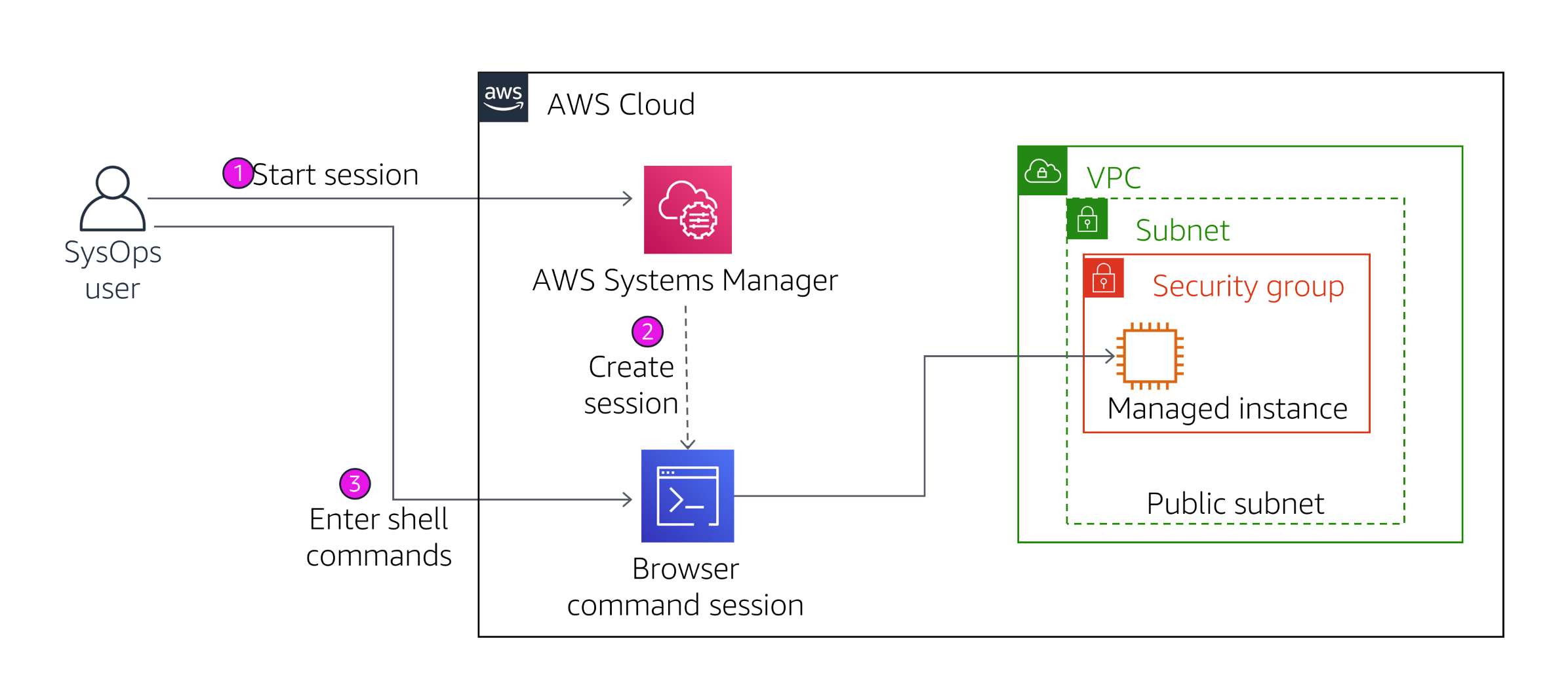
Session Manager Security Features
AWS Systems Manager Session Manager provides secure and auditable instance management without requiring SSH access. It offers an interactive one-click browser-based shell or CLI access to EC2 instances, eliminating the need to open inbound ports, maintain bastion hosts, or manage SSH keys.
Hands-On Experience
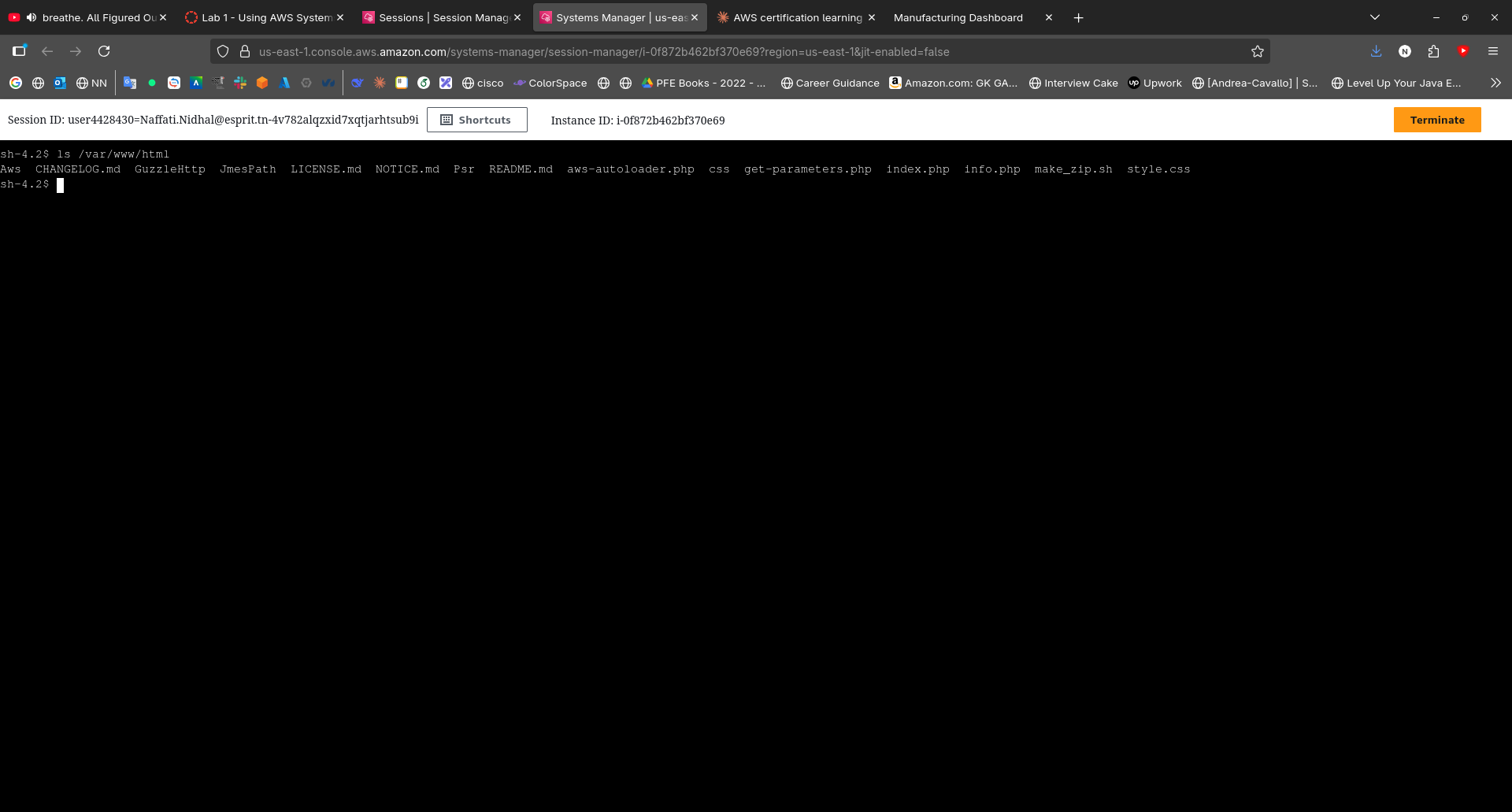
During the lab, I accessed the managed instance through Session Manager:
- Started a session from the Systems Manager console
- Ran commands on the instance through the browser interface
- Verified application files were installed in
/var/www/html - Demonstrated that traditional SSH access was not required by checking that port 22 wasn't open
Security and Compliance Benefits
- No Open Ports: Eliminates the need to open SSH ports (22) in security groups
- IAM Policy Enforcement: Access control through IAM policies rather than key management
- Audit Trail: Session Manager logs all commands in AWS CloudTrail
- Cross-Platform Access: Works consistently across Linux and Windows instances
- Session Recording: Commands and output can be recorded for compliance purposes
Real-World Applications
The skills and tools explored in this lab have immediate practical applications:
- Centralized Patching: Use Run Command to apply security patches across your entire fleet simultaneously
- Configuration Management: Leverage Parameter Store to manage application settings dynamically
- Compliance Auditing: Use Inventory to maintain compliance reporting across your infrastructure
- Secure Operations: Implement Session Manager to eliminate SSH access and improve security posture
Certification Preparation Insights
This lab reinforced several key concepts that are crucial for AWS Cloud Operations certification:
- Infrastructure as Code: Systems Manager documents provide a declarative way to manage infrastructure state
- Security Best Practices: Emphasis on least-privilege access and elimination of traditional access methods
- Operational Excellence: Focus on monitoring, automation, and consistent operational processes
- Cost Optimization: Centralized management reduces operational overhead and potential human error
Conclusion
AWS Systems Manager provides a comprehensive platform for managing your AWS resources at scale. The combination of Inventory, Run Command, Parameter Store, and Session Manager creates a powerful operational toolkit that enhances both security and efficiency.
The hands-on experience with these services has significantly improved my understanding of operational best practices in AWS, particularly around automation, security, and centralized management. These tools are essential for anyone pursuing the AWS Cloud Operations certification or working in operational roles within AWS environments.
For organizations looking to improve their operational practices, Systems Manager offers a path to eliminate traditional, less secure methods of instance management while providing powerful automation capabilities. The next step in my certification journey will involve exploring more advanced Systems Manager features and integration with other AWS services.
This blog post is part of my AWS Cloud Operations certification journey series. Stay tuned for more hands-on experiences and insights as I progress through the certification requirements.